5 min to read
Why new session should be created during user authentication?
Security POV

Let’s Understand a few Terms before jumping to our main topic viz “Why do we need a new session for user authentication”?
What’s Session?
In layman term session is the term used to refer to a user’s time browsing a webpage.It identifies the users to the app after they have logged in an is valid for a period of time. It contians activities like Page rendering, events e.g like, share, comments in session storages.
A web session is the sequence of network HTTP request and response transcations associated with the same user.WebApps/Websites use sessions once user has authenticated .This ensure the ability to identify the user on any subsequent requests as well as being able to apply security access controls, authorised access to the user private data and to increase usability of App. That’s why sessions can be used both pre and post authentication.
Since HTTP is a stateless protocol,which means each request and response pair is independent of other web interactions.
Now let’s understand Session Fixation Here don’t get confused session fixation with session Hijacking. In Session Hijacking steals the established session between the client and web server after the user logs in but in Session Fixation attack fixes an established session on the victim’s browser so the attack starts before the user logs in .
As per OWASP documentation
Session Fixation is an attack that permits an attacker to hijack a valid user session. The attack explores a limitation in the way the web application manages the session ID, more specifically the vulnerable web application. When authenticating a user, it doesn’t assign a new session ID, making it possible to use an existent session ID. The attack consists of obtaining a valid session ID (e.g. by connecting to the application), inducing a user to authenticate himself with that session ID, and then hijacking the user-validated session by the knowledge of the used session ID. The attacker has to provide a legitimate Web application session ID and try to make the victim’s browser use it.
Session Fixation Attack Workflow
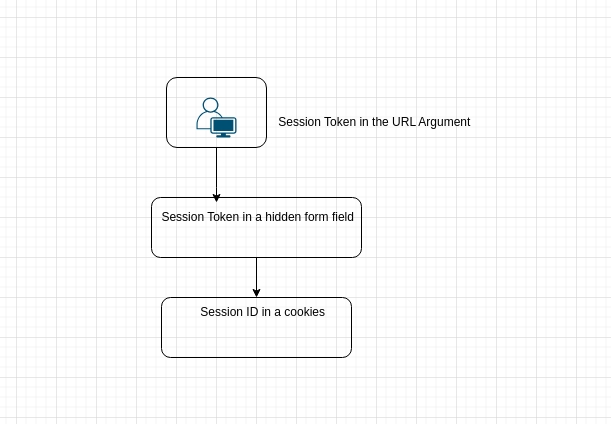
Here are the points rephrased into bullet points:
- Session token in the URL argument:
- The Session ID is sent to the victim in a hyperlink.
- The victim accesses the site through the malicious URL.
- Session token in a hidden form field:
- The victim is tricked into authenticating on the target Web Server.
- A login form developed by the attacker is used.
- The form could be hosted on the attacker’s web server or embedded in an HTML-formatted email.
Session ID in a cookie:
- Client-side script
Most browsers support the execution of client-side scripting. In this case, the aggressor could use attacks of code injection as the XSS (Cross-site scripting) attack to insert a malicious code in the hyperlink sent to the victim and fix a Session ID in its cookie. Using the function document.cookie, the browser which executes the command becomes capable of fixing values inside of the cookie that it will use to keep a session between the client and the Web Application.
META Tag
Is considered a code injection attack, however, different from the XSS attack where undesirable scripts can be disabled, or the execution can be denied. The attack using this method becomes much more efficient because it’s impossible to disable the processing of these tags in the browsers.
HTTP header response-
This method explores the server response to fix the Session ID in the victim’s browser. Including the parameter Set-Cookie in the HTTP header response, the attacker is able to insert the value of Session ID in the cookie and sends it to the victim’s browser.
What is the potential impact?
- Impersonation : Attackers can use a fixed session ID to impersonate victims, gaining unauthorized access to accounts and performing malicious actions or transactions.
- Data Breach : Access to a user’s session can expose sensitive data, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious activities.
- Privilege Escalation : Attackers can use session fixation to gain higher privileges within a web application, bypassing access controls and potentially compromising the entire system.
How to fix it ?
User authentication,it’s a crucual to generate the session identifier to prevent fixation attacks. Using passport req.session.regenerate() method we can ensure that after successful authentication, each user is assigned to a new unique session ID .
Non compliant Code
app.post('/login',
passport.authenticate('local', { failureRedirect: '/login' }),
function(req, res) {
// Noncompliant - no session.regenerate after login
res.redirect('/');
});
Compliant Code
app.post('/login',
passport.authenticate('local', { failureRedirect: '/login' }),
function(req, res) {
let prevSession = req.session;
req.session.regenerate((err) => {
Object.assign(req.session, prevSession);
res.redirect('/');
});
});
Behind the scene, how session fixation protection works?
- Session Creation:
- When a user visits a website or logs in, a session with a unique identifier is created.
- This identifier is stored in a cookie or passed through URL parameters.
- Session Fixation Attack:
- An attacker tricks the user into using a predetermined session ID.
- This allows the attacker to gain unauthorized access to the user’s session.
- Protection Mechanisms:
- Upon successful authentication, a new session ID is generated.
- The old session ID, potentially manipulated by the attacker, is invalidated.
- This ensures the attacker cannot use the fixed session ID.
- New Session ID:
- The user is assigned a new session ID for subsequent requests.
- This new ID is stored in a new session cookie or passed through URL parameters.


Comments